Teachers’ Attitudes, Beliefs and Teaching Quality on Student Outcomes
Tagged: Arts & Humanities
Introduction
Background
Empirical research previously executed to find out the purpose of education has focused on evaluating how teachers’ attributes impacted student performance (Blazar & Kraft, 2017). However, there is enough evidence that highlights the fact that student learning is usually multidimensional where many factors apart from their key academic knowledge is vital in making contributions to their short and long-term success. For example, psychologists have found that emotions, as well as personality influence the student thought process on the whole (Rodrigo-Ruiz, 2016), and the level to which student imbibe learning. Findings from previously conducted longitudinal studies have indicated a strong predictive power of childhood measures like persistence, motivation, self-control and emotional stability on career outcomes and health (Schoon et al., 2015). In fact, attitudes and behaviours act as strong predictors for some longterm learning outcomes.
In line with these findings, over the years teaching has been attributed using theories as having several dimensions. There are high expectations from teachers who provide high quality teaching to not only improve students’ academic scores but it is also expected that teachers provide emotionally supportive learning environments. This would be a key contributor to develop students socially and emotionally on the whole, manage classroom behaviours, offer accurate content, and encouraging critical thinking. Student outcome over a long-term period tends to be impacted by these aspects (Adler, 2016).
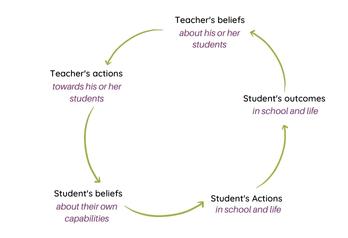
Problem Statement
Students’ academic achievements are considered as a key indicator of excellent academic performance and initiatives in education are generally aimed at achieving high level of achievement in school. There has been an increase in the engagement of teachers in identifying facets that influence students’ achievement. Many studies have investigated how factors linked with student attributes such as; intelligence, motivation and attributes etc., impact their overall performance (Hirokawa, 2018; Verma & Yadav, 2020).
For many years now, educators have discussed about variables that influenced student achievement. As per early research, it has been indicated that school environment has little impact on student achievement, not considering students’ family or societal background (Suhaini, 2020). Nonetheless, evidence exists which indicate that teachers qualification could also play a vital role in student outcomes (Antony & Elangkumaran, 2020). As far as teachers’ attributes or factors are concerned, the findings from a study revealed that student achievement improved when teachers were highly experienced (Alonge et al., 2020). Whereas, another study carried out by Igberadja (2016), revealed that overall achievement of students would be impacted adversely when institutions failed to provide technologically skilled teachers. Further, with regards to attributes of teachers, it has been reported by that attributes of teachers’ made an impact on achievement of students (Bhai & Horoi, 2019).
Education policies within India have concentrated largely on augmenting students’ attainment levels at school with the intention of increasing access to and participation in schools. Regardless of the increase in the number of enrollments, education quality as measured by students’ cognitive skills, continue to be poor. Schooling quality nonetheless, has achieved a balance between input parameters such as traits of teachers, infrastructure at school etc., in policy as compared to outcome measures such as student achievement scores. Over the period of the past ten years, it has been confirmed through research that teachers significantly influence the academic and life-long success of students. Several intensive initiatives have been undertaken to determine the contribution of teachers, or particular traits of teachers which substantially impact student outcomes.
Nonetheless, it is evident that extant literature has not investigated how teachers’ attitudes, beliefs and teaching quality influence student outcomes. Studies conducted thus far have only investigated how teachers’ experience, behaviours, and traits have individually impacted student performance. This presents an apparent gap in the literature which needs to be bridged. This research intends to bridge this gap by investigating how teachers’ attitudes, beliefs and teaching quality impact student performance.
Research Aims and Objectives
The aim of this particular research is to investigate how the beliefs, attitudes and quality of teaching shape student perceptions and how it impacts student outcomes.
Research Objectives
- To investigate the impact of teacher attitudes and beliefs on student outcomes.
- To examine how teaching quality influences student outcomes.
- To offer recommendations to further enhance student outcomes.
Research Questions
- How does teachers’ attitude and beliefs impact student outcomes?
- How does teaching quality influence student outcomes?
- What recommendations can be offered to further enhance student outcomes?
Research Significance
Existing research has revealed that changing attitudes, beliefs and behaviours of teachers are not an easy task. Given the situation, there is a possibility that in the event of a conflict between teachers’ beliefs and attitudes and school curriculum, the issue of ensuring quality could be challenging. This is what makes up the core of this research. The purpose of this research is to investigate how individual factors of teachers’ like instruction quality, behaviours, beliefs and attitudes influence student outcomes. As it has been mentioned previously, a large number of extant research in the domain only concentrates on specific facets such as quality, attitudes etc. However, previous researches have not holistically investigated the said aspects. Therefore, the key significance of this research would be that it intends to holistically investigate these aspects on student outcomes. Furthermore, most of the research carried out within the domain have been conducted either in developed nations like the United Kingdom, United States or the MiddleEastern and African regions. But, this present research will be executed in India. The findings that will be derived through this research will offer novel insights into how teaching quality, teachers’ beliefs and attitudes would influence student outcomes. Based on this, robust measures can be undertaken to enhance the quality of teaching and remedial steps can be initiated to modify the attitudes and beliefs of teachers. Lastly, this research will largely contribute to the extant literature and would prove to be of much significance for future researchers.
Chapter Scheme
This research will be strategically segregated into five chapters which includes; Introduction, Literature Review, Research Methodology, Results, and Discussion and Conclusion (Chapters 1 to 5 respectively). The introduction chapter will present a brief background, outline the problem statement and research objectives while indicating the significance of the research. The literature review chapter will conduct a review of the existing literature and identify inherent gaps. The research methodology chapter will outline the methodology chosen for this research and also present insights into data collection and analysis. The results chapter will present the findings from the data analysis and lastly the discussion and conclusion chapter will discuss the findings derived with findings from other researches and arrive at a conclusion.
References
- Adler, A. (2016). ScholarlyCommons Teaching Well Being increases Academic Performance Evidence Teaching Well Being increases Academic Performance Evidence From Bhutan. https://repository.upenn.edu/edissertations/1572/
- Alonge, B. D., Olayinka, K. A., Francis, A. O. V. F. A., & Oluwakemi, A. (2020). Teachers Teaching Experience and Educational Qualification as Correlates of Academic Performance of Students in Public Secondary Schools in Ekiti State, Nigeria. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/287193057.pdf
- Antony, S., & Elangkumaran, P. (2020). An Impact on Teacher Qualifications on Student Achievement in Science: A Study on the GCE (O/L) in Trincomalee District. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/ElangkumaranPeriyathamby/publication/346476396_An_Impact_on_Teacher_Qualifications_on_Stude nt_Achievement_in_Science_A_Study_on_the_GCE_OL_in_Trincomalee_District/links/ 5fc47961458515b797895b8d/An-Impact-on-Teacher-Qualifications-on-StudentAchievement-in-Science-A-Study-on-the-GCE-O-L-in-Trincomalee-District.pdf
- Bhai, M., & Horoi, I. (2019). Teacher characteristics and academic achievement. Applied Economics, 51(44), 4781–4799. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2019.1597963
- Blazar, D., & Kraft, M. A. (2017). Teacher and Teaching Effects on Students’ Attitudes and Behaviors. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 39(1), 146–170. https://doi.org/10.3102/0162373716670260
- Hirokawa, S. (2018). Key attribute for predicting student academic performance. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Education Technology and Computers - ICETC ’18, 308–313. https://doi.org/10.1145/3290511.3290576
- Igberadja, S. (2016). Effects of teachers ‘gender and qualification on students ‘performance in vocational technical education. Journal of Technical Education and Training, 8(1). http://penerbit.uthm.edu.my/ojs/index.php/JTET/article/view/1145
- Rodrigo-Ruiz, D. (2016). Effect of teachers emotions on their students: Some evidence. Journal of Education & Social Policy, 3(4), 73–79. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Debora-RodrigoRuiz/publication/311949229_Effect_of_Teachers’_Emotions_on_Their_Students_Some_ Evidence/links/58641bde08ae8fce490b724d/Effect-of-Teachers-Emotions-on-TheirStudents-Some-Evidence.pdf
- Schoon, I., Nasim, B., Sehmi, R., & Cook, R. (2015). The impact of early life skills on later outcomes. https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10051902/
- Suhaini, M. (2020). Factors Influencing Student Achievement: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 24(5), 550–560. https://doi.org/10.37200/IJPR/V24I5/PR201720
- Verma, S., & Yadav, R. K. (2020). Effect of Different Attributes on the Academic Performance of Engineering Students. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Advent Trends in Multidisciplinary Research and Innovation (ICATMRI), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICATMRI51801.2020.9398442

