The theory, concepts and tools used for multilevel models for cloud based application
Brief highlights
- Cloud computing has been gaining considerable attention for different industries.
- The occurrence of large volumes of data has made it necessary to process and store the required data.
- This large volume of data cannot be processed by a single computer or a small group of computers.
- Thus the falling costs of hardware and abundant data availability are the key forces that motivate to use cloud computing.
Background
Cloud computing has nowadays become an inseparable part of the different academia industries. Employing large number of networked devices, using different internet services etc activities have resulted in generation of large volumes of data which requires processing as well as storage in order to be used further (Ahson & Ilyas, 2010). This processing and storage of data is sometimes not possible by single computer and hence requires integration of large number of computers in specially designed accommodations, data centres. Cloud computing has enabled to use a large number of resources and thus facilitated resolving issues arising in different domains. Data intensive or data computing applications are the key applications that exploit cloud computing and associated cloud technologies.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be defined as a technology that facilitates easy and on-demand access to a number of configurable computing resources which can be arranged and provided by the service provider. This reduces the effort of the users and thus the users need not be bothered about specifications of technology being used while deploying their application as these aspects are manage by the cloud service provider (CSP) (Erl et al., 2013). The CSP can decide a particular price that the users need to pay in order to access the service provided. The CSP ensures that the service demanded by the users is provided as per their demand and also takes care of the other allied complex operations. It assures access of entire system to the user and thus provides the resources required by them for executing their applications and managing the complete flow of system.
Cloud computing has been labelled as Greener Computing Alternative due to its facilities such as access to a pool of resources and thus enabling a reduction in the costs for company. Some of the studies conducted by AT&T have identified the positive impact of the technology on environment.
Different models of cloud
The models of a cloud are generally categorized into two types; service models and deployment models (Kulkarni et al., 2012). There are three models of service in cloud. They are:
- Software as a service (SaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Similarly, there are three deployment models in cloud. They are:
- Private cloud
- Public cloud
- Hybrid clouds
The figure given below illustrates the different models of cloud.
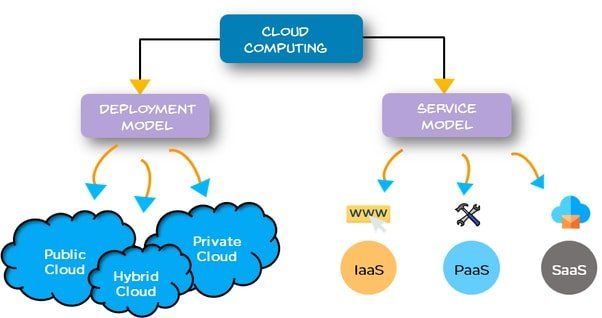
Figure 1 Different models of cloud
Cloud service models
As mentioned earlier there are three service models of cloud (Bokhari et al., 2016). They are described as follows.
Software as a service (SaaS): This model of the cloud enables the end users to use and rent the applications from the CSP without downloading them on their systems. This implies that the licensed applications used by end users are actually installed on cloud infrastructure and are being used by the users through interface of thin/thick clients such as Google chrome, internet explorer etc. Thus this model of cloud is specially used by users so that the users can use and access the applications that are made available CSPs (Gibson et al., 2012). Besides some particular users who have their own configurations defined only CSP will be able to control and manage the infrastructure. One of the challenges that SaaS model poses is slow of the network causing slowing the time of processing for heavy weight applications such as 3D games.
Advantages of SaaS
- Lesser software licensing cost
- Applications on SaaS can be used by multiple users at a time because SaaS is based on one-to-many concept.
- Controlling and managing applications is the responsibility of CSP.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): As the name implies this service model supplies a suitable environment to the developer for developing applications and software for deploying them via internet. This model eases the process for developers by eliminating the need for managing development environment (Khurana & Verma, 2013). In this model the user has no control over the infrastructure of cloud but can manage the application deployed.
Advantages of PaaS
- Provides higher flexibility for development process
- Follows one-to-many principle and thus multiple developers can work on one application.
- It allows the users to control the application developed by them and also allows creating new platform if required.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This model of cloud supplies virtual infrastructure and raw hardware which can be helpful for creating, managing and destroying storage. In other words it provides users a virtual server in addition to one or more than one CPU which executes different operations or tasks. Some service providers are permitting virtual instances to be connected with the network of companies through virtual private network (VPN) enabling the company to show itself as a big scalable IT infrastructure.
Advantages of IaaS
- The client or users are able to increase or decrease the infrastructure as per their requirement.
- Minimizes the cost of human resources and hardware.
Cloud deployment models
There are three deployment models of cloud (Diaby & Rad, 2017). They are described as follows.
Private cloud: This model is meant especially for the company and cannot be accessed by the public. Thus it is called as private cloud. This cloud offers maximum data security.
Public cloud: This model offers many features such as data storage etc which are facilitated by service providers. It is based on pay-as-you-use model.
Hybrid cloud: This cloud model as the name suggests includes features of both private as well as public cloud.
Summary
Cloud technology can be defined as a model that identifies the issues associated with reliability and quality of service. Contrary to the traditional computing techniques, the tools and technologies used or involved in cloud computing help in computing intensive data operations at attractively low prices.
References
- Ahson, S.A. & Ilyas, M. (2010). Cloud computing and software services: theory and techniques. [Online]. CRC Press. Available from: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=k2TakPufj-cC&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=++Syed+A.+Ahson+and+Mohammad+Ilyas,+Cloud+computing+and+software+services:+Theory+and+Techniques.&ots=LkO3NCeSrD&sig=HOYm1rft0n7968JDcIwzhWYSINc.
- Bokhari, M.U., Shallal, Q.M. & Tamandani, Y.K. (2016). Cloud computing service models: A comparative study. In: 2016 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom). [Online]. 2016, IEEE, pp. 890–895. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7724392/.
- Diaby, T. & Rad, B.B. (2017). Cloud Computing: A review of the Concepts and Deployment Models. International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science. [Online]. 9 (6). p.pp. 50–58. Available from: http://www.mecs-press.org/ijitcs/ijitcs-v9-n6/v9n6-7.html.
- Erl, T., Puttini, R. & Mahmood, Z. (2013). Cloud computing: concepts, technology & architecture. [Online]. Pearson Education. Available from: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=++Erl%2C+T.%2C+Puttini%2C+R.%2C+%26Mahmood%2C+Z.+Cloud+Computing%3A.
- Gibson, J., Rondeau, R., Eveleigh, D. & Tan, Q. (2012). Benefits and challenges of three cloud computing service models. In: 2012 Fourth International Conference on Computational Aspects of Social Networks (CASoN). [Online]. 2012, IEEE, pp. 198–205. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6412402/.
- Khurana, S. & Verma, A.G. (2013). Comparison of cloud computing service models: SaaS, PaaS, IaaS. IJECT. [Online]. 4 (Spl-3). Available from: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Khurana%2C+S.+and+Verma%2C+A.G.%2C+2013.+Comparison+of+cloud+computing+service+models%3A+SaaS%2C+PaaS%2C+Iaa.
- Kulkarni, G., Chavan, P., Bankar, H., Koli, K. & Waykule, V. (2012). A new approach to Software as Service Cloud. In: 2012 7th International Conference on Telecommunication Systems, Services, and Applications (TSSA). [Online]. 2012, IEEE, pp. 196–199. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6366050/.

 Next Post
Next Post