Future Research Directions on Opportunistic Routing in Wireless Mesh Networks
What is a wireless mesh network?
- The communication networks consisting of wireless nodes arranged in a mesh topology are known as wireless mesh networks (WMNs). A mesh topology is the interconnection of the nodes in the network that are connected to each other, resulting in a mesh-like structure.
- Devices in wireless mesh networks include clients, gateways, routers and nodes, and each device serves to transfer the data.
- The network is decentralised, and only forwarding data to the neighbouring node is possible, thereby simplifying the network structure.
- Wireless Mesh Network enables people working in remote areas to stay connected to the internet (Rejina, 2020).
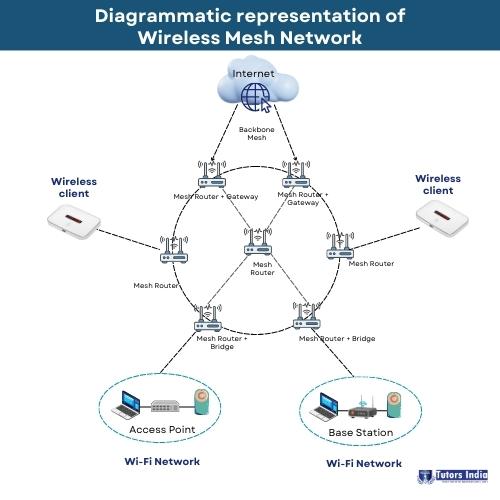
Figure : Diagrammatic representation of Wireless Mesh Network
What is opportunistic routing?
- Opportunistic routing (OR), also called diversity forwarding or any path routing, is a relatively new area for wireless networks wherein the node closest to the target node is used for forwarding the data, making OR a possible future power network.
- Unlike traditional routing, OR selects an ordered group of nodes as possible next-hop forwarders rather than a single specific node to be the next-hop as a forwarder for a packet.
- The efficiency, throughput, and reliability of sensor networks have been improved due to opportunistic routing. Many energy-saving strategies have been established in wireless networks using opportunistic routing to extend network lifetime (Jadhav, 2016).
- Studies on OR have primarily focussed on wireless sensor networks. This blog will focus on the research directions and prospects of OR in wireless mesh networks.
Research on Opportunistic routing in Wireless Mesh Networks
Research has been conducted on the applications of Opportunistic routing in Wireless Mesh Networks in the field of Computer Science and Information Technology. The research focussed on:
- Performance Modelling
- Candidate Selection Algorithms
- Distance Progress based Opportunistic routing, and
- Multicast-based opportunistic routing
Performance Modelling
- A Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) was used to analyse the performance of Wireless Mesh Networks that may be achieved using Opportunistic Routing.
- The nodes represent the states of the chain, and the state transitions represent how the packet moves through the network. This model yields a discrete phase-type distribution with straightforward equations for distribution and moments.
- In a typical scenario, Opportunistic Routing can lower the estimated number of transfers by 20% or more.
- Opportunistic routing also significantly reduced the number of transmissions, which is especially important for networks requiring Quality of Service (QoS)(Mazumdar, 2013).
Candidate selection
- The primary goal of OR protocols is to reduce the number of transmissions from a source to a particular destination. The candidate selection method is a critical issue in OR for achieving this goal.
- A new local-based and speedy candidate selection process was proposed based on the link delivery probability from one node to a candidate node.
- A new approach, the Heuristic Candidate Selection algorithm, based on Optimum Delivery Probability (HU-COP), discovers candidates whose link delivery probabilities are similar to the link delivery probabilities of optimum candidates.
- According to the results, HU-COP outperforms the well-known ExOR. Furthermore, the performance results of HU-COP in many settings are quite near to the results of the optimal algorithm. Furthermore, HU-COP identifies candidate sets significantly more quickly (Darehshoorzadeh, 2014).
Distance Progress-based Opportunistic Routing
- Distance Progress Based Opportunistic Routing (DPOR) is an opportunistic routing system that prioritises relay nodes based on their distance progress to the destination.
- The purpose of DPOR is to maximise the likelihood of successful data delivery by selecting nodes that make significant progress towards the destination in each transmission attempt.
- DPOR is a fast and efficient algorithm for selecting candidates. DPOR requires much lesser information than other types of OR.
- The main advantage of DPOR is that it considers the dynamic movement of nodes and chooses relay candidates who are more likely to carry the data closer to the destination.
- This can assist in reducing voids (areas with no functional relay nodes) and enhance overall delivery rates in opportunistic networks (Darehshoorzadeh, 2012).
Multicast based Opportunistic Routing
- Multicast based opportunistic routing is a type of opportunistic routing that was developed to transport multicast traffic efficiently on wireless networks.
- Multicast communication simultaneously delivers data packets from a source node to several destination nodes.
- The source node transmits multicast data packets to its close neighbours in multicast-based opportunistic routing.
- Instead of selecting a single best relay node, like in unicast opportunistic routing, multicast-based opportunistic routing uses wireless communication’s broadcast nature and the presence of several potential receivers.
- Research on multicast-based opportunistic training involved proposing a scheme to maximise video reception quality. A dynamic algorithm was developed, and the results have shown improvement in the multicast network compared to the existing schemes (Li, 2018).
Future Research Directions
Wireless Mesh Networks have been proposed as one of the primary choices for the future generation of wireless networking. Opportunistic Routing has been presented as an approach to using the unique characteristics of wireless networks by selecting various nodes for forwarding the message, significantly improving the performance of Wireless Mash Networks.
The following are the possible future directions for Opportunistic Routing in Wireless Mash Networks:
- Two things are critical for the effective implementation of Opportunistic routing: candidate selection and candidate coordination. For improving the efficiency of WMNs, a correct candidate selection is a must. Research focussing on improving candidate selection is needed.
At the same time, candidate coordination cannot be ignored, for improper candidate coordination may result in reduced efficiency of the OR protocol. Research focussing on improving candidate coordination using existing technologies is needed by developing suitable algorithms.
- Research could be done for WMNs where the nodes do not have mobility.
- Another research direction is using the OR approach for broadcasting a packet to all nodes in the networks.
- Research on developing safe OR protocols and incorporating them into the existing security structures to create a more robust and secure information delivery service can be considered (Kafaie, 2018).
Conclusion
Wireless Mash Networks are communication networks where the devices or nodes are connected in a mesh-like structure. In opportunistic routing, the node closest to the target node is used for forwarding data. The applications of opportunistic routing in wireless mesh networks focussed on performance modelling, candidate selection, distance progress based opportunistic routing and Multicast based opportunistic routing. Future research can be done on improving candidate selection and candidate coordination, developing safer opportunistic routing protocols, wireless mesh networks with no mobility and broadcasting a packet to all nodes in the network.
About Tutors India
We are a team of qualified researchers and academicians who offer assistance with Master’s dissertations. We assist students specialising in computer science with programming and algorithms. We help clarify concepts related to dissertation computer science, such as programming languages, python programming and object oriented programming. We also offer dissertation algorithm tips for students that help them develop highly effective ones. We ensure the dissertation help offered to students complies with the university’s specifications.
Check out our example of A Study on Cloud Computing: Challenges and Security Issues to know how a dissertation in computer science is written.
We also assist students from other disciplines, like nursing, psychology, finance, law and arts, with their dissertations. To know more about how a dissertation is written in those specialisations, check out our dissertation examples.
References
- Rejina Parvin, J. (2020). An Overview of Wireless Mesh Networks. In Wireless Mesh Networks – Security, Architectures and Protocols. IntechOpen.
- Jadhav, P., & Satao, R. (2016). A survey on opportunistic routing protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks. Procedia Computer Science, 79, 603–609.
- Mazumdar, A.P., Sairam, A.S. (2013). On Performance Modeling of Ad Hoc Opportunistic Routing Protocols. In: Woungang, I., Dhurandher, S., Anpalagan, A., Vasilakos, A. (eds) Routing in Opportunistic Networks. Springer, New York, NY.
- Darehshoorzadeh and A. Boukerche, “An efficient heuristic candidate selection algorithm for Opportunistic Routing in wireless multihop networks,” 2014 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Funchal, Portugal, 2014, pp. 1-6.
- Darehshoorzadeh and L. Cerdà-Alabern, “Distance Progress Based Opportunistic Routing for wireless mesh networks,” 2012 8th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Limassol, Cyprus, 2012, pp. 179-184. .
- Li, H. Xiong, J. Zou and D. O. Wu, “Joint Dynamic Rate Control and Transmission Scheduling for Scalable Video Multirate Multicast Over Wireless Networks,” in IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 361-378, Feb. 2018.
- Kafaie, Y. Chen, O. A. Dobre and M. H. Ahmed, “Joint Inter-Flow Network Coding and Opportunistic Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mesh Networks: A Comprehensive Survey,” in IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 1014-1035, Secondquarter 2018.

 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post